Centrifugal Air Compressor is commonly used in chemical production of a high-speed rotating equipment, which through high-speed rotation, generating centrifugal force, so that the gas in the impeller of the air compressor pressure expansion flow, from the impeller out of the gas flow rate, the pressure has been correspondingly increased, and then realize the compressed air. In the process of Centrifugal Air Compressor, often produces some faults, affecting its working effect, affecting chemical production, this paper centrifugal air compressor produces the reasons for failure to analyze, and then take effective measures to deal with its faults, improve the working effect of centrifugal air compressor.
01. Abnormal vibration and noise
Q : Misalignment
A: Remove the coupling and rotate the compressor independently. If there is no abnormal vibration when the compressor is rotating, the malfunction may be caused by misalignment; check the alignment and refer to the installation instructions.
Q: Compressor rotor imbalance
A: Check the rotor to see if the problem is caused by dirt or damage: rebalance the rotor if necessary.
Q: Impeller Damage
A: Check the impeller and repair or replace if necessary.
Q: Bearing irregularities
A: Check the bearing, adjust the clearance, and repair or replace if necessary.
Q: Coupling failure or imbalance
A: Check coupling balance, check coupling bolts and nuts.
Q: Seal ring defective
A: Check and measure seal ring clearance, repair or replace if necessary.
Q: Abnormal oil pressure or temperature
A: Check and measure the sealing ring gap, and check the oil pressure, oil temperature, and oil system operation at each injection point, and make adjustments if abnormalities are found. Repair or replace if necessary.
Q: Dirt in the oil is not clean, causing bearing wear.
A: Identify the source of dirt, check the oil quality, add filtration, change the oil regularly, check the bearings, and adjust the clearance.
Q: Wheezing
A: Check to see if the compressor is running away from the surge point, if the anti-surge margin is correct, and if the anti-surge device is working properly.
Q: Stress in the gas line is transferred to the casing, causing misalignment.
A: Gas lines should be well secured to prevent excessive stress on the compressor cylinder: the lines should have sufficient elastic compensation to handle thermal expansion.
Q: If there are other equipment operating in the vicinity of the compressor
A: Separate their tombstone bases from each other and increase the elasticity of the connecting pipes.

02. Thrust bearing failure
Q: Excessive axial thrust
A: Check the thrust bearing clearance, check the gas inlet/outlet differential, check the internal seal ring gap data for exceeding the standard if necessary, and check the balance disk seal ring gap between segments for exceeding the standard.
Q: Lubrication is not normal
A: Check the oil pump, oil filter and oil cooler, check the oil temperature, oil pressure and oil most, check the oil quality.

03. Oil sealing ring and sealing ring failure
Q: Misalignment and vibration
A: Refer to Vibration section
Q: Dirt in oil
A: Check the oil filter and replace the filter element with dirt; enhance in-line filtration.
Q: Seal ring gap deviation
A: Check the gap and adjust or replace if necessary.
Q: Insufficient oil pressure
A: Check the reference air pressure, which should not be lower than the minimum limit value.
Q: Insufficient precision of sealing ring
A: Check the sealing ring and repair or replace if necessary.
Q: Insufficient sealing oil quality and oil temperature.
A: Check the oil quality and temperature and solve the problem.

04. The sealing system does not work stably or normally.
Q: Seal ring precision is not enough
A: Check the oil quality and oil temperature, and check the sealing ring, and repair or replace it if necessary. If necessary, repair or replace the seal ring and solve the problem.
Q: The quality of sealing oil or oil temperature does not meet the requirement.
A: Check the sealing oil quality and replace it if it does not meet the specifications; check the sealing oil temperature and adjust it.
Q: Differential oil and air pressure system is not working well.
A: Check the reference air pressure and line, and adjust to the specified value; check the working condition of each component of differential pressure system.
Q: Worn or damaged seals
A: Remove seals and readjust gap assembly: Repair or replace as specified.
Q: Uneven contact wear on float ring seat.
A: Grind, repair or replace with new parts.
Q: Float seat end face is chipped or sealing surface is worn.
A: Eliminate suction damage, reduce wear, and replace with new parts if necessary.
Q: Seal ring broken or damaged (assembly damage or thermal stress damage during idling) A: Damage may be caused during assembly, attention should be paid to assembly; minimize no-load operation: replace if not repairable.
Q: Corrosion of sealing surfaces, seals and O-rings.
A: Analyze the nature of the air break, change the material of the parts or replace with new spare parts.
Q: Seal icing due to low temperature operation.
A: Eliminate icing, or use dry nitrogen to purify the sealing atmosphere.
Q: Measuring instrument working error
A: Check the system's measurement instrumentation, found to be out of order when overhauling or replacement.
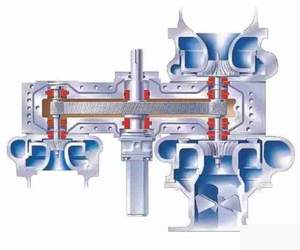
05. Performance does not meet the requirements
Q: Design error
A: Check the measurement of the system to review the original design, check whether the technical parameters are in line with the requirements; if found problems should be negotiated with the seller and manufacturer.
Q: Manufacturing error
A: Check the original design and manufacturing process requirements: check the material and machining accuracy: if problems are found, negotiate with the seller and the manufacturer.
Q: Difference in gas properties
A: Check the gas property parameters, if the gas property is too different from the original design, it will affect the performance index of the compressor: try to solve the problem according to the actual needs and possibilities.
Q: Changes in operating conditions
A: If the actual running conditions are too different from the design conditions, the running performance of the compressor is bound to deviate from the design performance, and the reason should be found out if any abnormality is found.
Q: Seal ring gap is too large
A: Check the gap of each part, and adjust or replace them if they do not meet the requirements.

06. Surge
Q: The operating point falls into the surge zone or is too close to the surge boundary.
A: Check the position of the operating point on the compressor characteristic line. If the operating point is too close to or falls into the surge zone, adjust the working condition and eliminate the surge.
Q: Insufficient setting of anti-surge margin
A: Determine in advance the anti-surge margin for each operating condition; the anti-surge margin line should be adjusted to the optimum.
Q: Insufficient suction flow
A: The inlet valve may not be open enough, the valve spool is too dirty or iced up, the inlet channel is blocked, the inlet air source is reduced or cut off, etc. The cause should be found out and solved. The cause should be investigated and solved.
Q: When the working condition changes, the bleeder valve or backflow valve is not opened in time.
A: If the inlet flow rate decreases or the speed drops, or if the speed rises rapidly, the cause should be identified: open the air release or return valve to prevent surge in a timely manner.
Q: Compressor outlet gas system pressure is too high.
A: When the compressor is slowed down or stopped, the gas is not released or returned; the outlet check valve is out of order or not tight, and the gas is backing up: identify the cause and take measures.
Q: Anti-surge device not automatic A: Anti-surge device should be automatic during normal operation.
Q: The anti-surge device or mechanism is out of alignment or malfunctioning.
A: Regularly check the operation of the anti-surge device. If it is found that the anti-surge device or mechanism is out of order or jammed, or does not function properly, solve the problem in a timely manner.
Q: The setting value of anti-surge device is not allowed
A: Strictly set the anti-surge value and test it regularly, and correct it if it is found to be inaccurate.
Q: Increase speed and pressure too fast
A: When the working condition changes, the speed and pressure should not be raised too violently or too quickly, but should be carried out alternately, slowly and evenly.
Q: Lowering speed before lowering pressure A: Lowering speed should be preceded by lowering pressure to avoid wheezing.
Q: Compressor parts are damaged when the nature of the gas changes or the state of the gas changes severely.
A: Before changing the nature or condition of the gas, the characteristic line should be converted, and the anti-surge value should be adjusted according to the changed characteristic line. Damaged or dislodged interstage seals, balancing disk seals, and O-rings will induce surge: they should be inspected frequently to ensure that they are in good condition.
Q: Compressor gas outlet line check valve not working
A: The non-return valve on the outlet gas line of the compressor should be inspected frequently to keep the operation flexible and reliable, so as to prevent gas from backing up when the speed is lowered or when the compressor is shut down.

07. Damaged impeller
Q: The material is unqualified and the strength is not enough. A: Re-examine the material used in the original design and manufacture, if the material is unqualified, the impeller should be replaced.
Q: Poor working conditions (loss of strength)
A: Working conditions do not meet the requirements of the hearing, due to poor conditions, resulting in a reduction in strength, should improve the working conditions, in line with the design.
Q: Excessive load, strength reduction A: Due to too high a speed or too large a flow rate or pressure ratio, the strength of the impeller is reduced, resulting in damage; prohibit severe overload or overspeed operation.
Q: Abnormal vibration, moving and static parts touching and bumping.
A: Excessive vibration, resulting in contact between the rotating part and the static part, touching and collision, resulting in damage; prohibit the vibration value is too large for forced operation; eliminate abnormal vibration.
Q: Falling debris
A: Compressor into the debris to break the impeller or other parts: strictly prohibit debris into the compressor, check whether the inlet filter is damaged.

08. Air Leakage
Q: Deposited inclusions
A: Keep the gas pure. Remove any deposits in the flow-through section and cylinder as soon as possible.
Q: Stress corrosion and chemical corrosion sealing system is not working well.
A: Prevent stress concentration from occurring, prevent harmful components from entering the compressor, and take anti-corrosion measures for the compressor. Check the components of the sealing system and find out the cause of the problem.
Q: O-ring failure
A: Check each O-ring and replace them if they are defective or deteriorated.
Q: Air leakage from cylinders or joints
A: Check the air joints and flange joints, and take prompt action if air leakage is found.
Q: Sealant failure
A: Check the sealant and packing on the center part of the cylinder and other parts of the cylinder, and replace them if they are found to be defective.
Q: Improper operation
A: Check whether the operation index is correct, check the running status of the compressor, and solve the problem when abnormalities are found.
Q: Seal ring damage, breakage, knee corrosion, wear and tear.
A: Check the sealing rings: find out the cause of breakage, damage, wear and corrosion. Repair or replace in time.

09. Insufficient flow and discharge pressure
Q: Problems with flow rate
A: Compare the discharge pressure and flow rate with the characteristic curve to see if they are in line with each other.
Q: Compressor reversal
A: Check the direction of rotation. The direction of rotation should match the direction of the arrow on the compressor housing.
Q: Low suction pressure
A: Check inlet filter
Q: Molecular weight discrepancy
A: Check the actual molecular weight of the gas measured at the inlet. If the actual molecular weight is smaller than the specified value, the discharge pressure is insufficient.
Q: Engine speed is lower than design speed
A: Check the compressor's operating speed against the manual; if the speed is really low, increase the prime mover speed.
Q: Circulating air from discharge side to suction side increases.
A: Check the circulating air volume, check the external piping, check the opening of the circulating air valve, and adjust if the circulating air is too large.
Q: Malfunction of manometer or flow meter
A: Check each gauge and adjust, repair or replace if problems are found.

10. Prime mover overload Q: Molecular weight larger than specified value
A: Check the actual molecular weight of the gas and compare with the design specification.
Q: Electrical problems with prime mover motor
A: Check the heat capacity most and action condition of circuit breaker; check whether the voltage is reduced; check whether the current difference of each phase is within 3%; find out the problem and solve it in time.
Q: The surface of the diffuser adjacent to the impeller is corroded, and the diffuser pressure is reduced.
A: Disassemble and inspect the diffuser flow paths, if there is corrosion, the material should be improved or the hardness of the surface should be increased, the surface should be cleaned and the surface should be smoothed, and the diffuser should be replaced if the impeller touches the diffuser or if the diffuser is deformed.
Q: Impeller or diffuser deformation
A: Deformation of impeller or diffuser should be repaired or replaced.
Q: The rotating part touches the stationary part.
A: Disassemble the prime mover compressor and gear box; check the clearance of each part and compare with the instruction manual: find out the problem and solve it in time.
Q: High suction pressure
A: If the suction pressure is high, the weight flow rate will increase and the power consumption will be high: check with the design data to find out the reason. Find out the cause and solve it. Centrifugal air compressor in daily operation, due to a variety of factors, resulting in its failure, so in its daily use, the need to strengthen the centrifugal air compressor maintenance and repair, and regularly overhaul its components. Centrifugal air compressor is a kind of equipment often used in chemical production, and its safety is related to the safety of chemical production, so in the process of daily work, strengthen the maintenance management, reduce the incidence of malfunction to ensure the safety of its operation.